AI coding agents are powerful, but they don't understand your monorepo out of the box. They don't know how your workspace is structured, what naming conventions your team follows, or how to run tasks the Nx way. That's why we're shipping Nx agent skills: portable capabilities that teach your AI agent how to work effectively in monorepos, in particular in combination with Nx.
Getting Started
❯
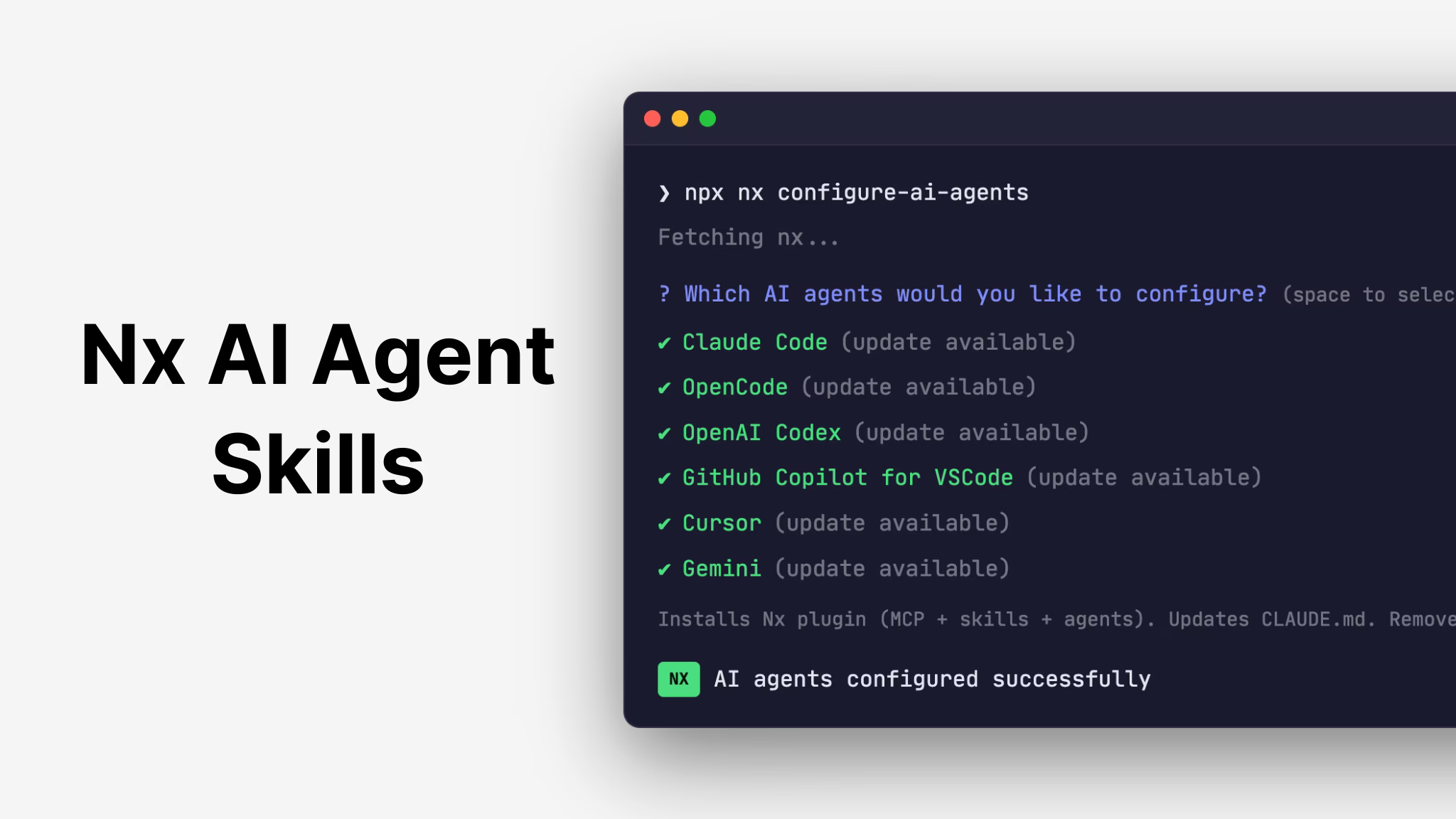
npx nx configure-ai-agents
This single command sets up everything your AI agent needs: an MCP server for talking to CI, a set of skills for working with your monorepo, and a CLAUDE.md / AGENTS.md with guidelines. It works across major AI coding tools: Claude Code, Cursor, GitHub Copilot, Gemini, Codex, and OpenCode. All configurations are generated from a single source of truth, so every AI tool gets the same capabilities.
You can also run npx skills add nrwl/nx-ai-agents-config via skills.sh. Note that this won't configure the Nx MCP server or install the Claude plugin.
Why Skills?
When we first shipped the Nx MCP server for Cursor, all AI agent capabilities were delivered as MCP tools. That was the only mechanism available at the time. But it made the MCP server bloated with tools that didn't actually need a server connection. Things like "how to explore the workspace" or "how to run a generator" are really knowledge and procedures.
We restructured. The Nx MCP server is now lean and focused on what MCP is actually for: connecting to remote services like Nx Cloud for CI status and Nx self-healing CI. Everything else moved to skills.
Skills are structured knowledge that teaches your AI agent how to perform specific tasks. Unlike dumping everything into a system prompt, skills are loaded incrementally, only when the agent actually needs them. This keeps your agent's context focused and efficient. Skills are procedural guides that agents follow using their existing tools (terminal, file system, etc.). Learn more at agentskills.io.
What's Included
Here's what ships with configure-ai-agents today:
Understand Your Workspace
The nx-workspace skill teaches your agent how to explore your monorepo structure using the Nx project graph. Instead of guessing project locations or reading random config files, the agent uses Nx CLI commands like nx show projects or nx graph to efficiently build up an understanding of your workspace.
It knows how to filter projects by type, tags, or patterns. It can find affected projects, trace dependencies, and understand target configurations. This is the foundation that other skills build on.
Bridge Local Dev and CI
This is the skill that enables fully autonomous workflows. We covered this in depth in our post on autonomous AI agent workflows (aka "Giga Ralph"), but here's the summary: the monitor-ci skill opens a communication channel between your local AI agent and Nx Cloud CI.
When your agent pushes a PR, it can:
- Monitor CI pipeline status in real-time
- Receive failure context from Nx Cloud
- Communicate with Self-Healing CI
- Apply verified fixes automatically
- Fully autonomously keep iterating until CI is green
Generate Code Predictably
This is where generators and AI form a powerful combination. We've written about this before: LLMs are great at understanding context and making decisions, but they struggle with consistency. Generators are the opposite: they produce identical, predictable output every time but lack the intelligence to know when and how to use them.
The nx-generate skill combines both. When you ask your agent to create a new library, it:
- Explores your workspace to learn conventions (naming, tags, directory structure)
- Finds the right generator and reads its schema to understand options
- Runs the generator with flags that match your existing patterns
- Verifies the output passes lint, test, and build
Here's what that looks like in practice. Ask your agent: "Create a new React feature library for tracking order delivery."
The agent first uses the workspace skill to discover existing libraries, checks their naming conventions and tags, then invokes the generator:
❯
nx g @nx/react:library \
❯
--directory=packages/frontend/orders/feat-delivery-tracking \
❯
--name=@tusky/feat-delivery-tracking \
❯
--tags="scope:orders,type:feature" \
❯
--no-interactive
The result follows the exact same structure as all your other feature libraries. Same naming convention, same tags, same directory placement. The generator handles the predictable scaffolding; the AI agent handles the intelligence of figuring out what to generate and where and also how to adapt it if necessary.
Use the Nx CLI Effectively
The nx-run-tasks skill teaches your agent how to run tasks properly through the Nx CLI: single tasks (nx run), multiple tasks (nx run-many), and affected tasks (nx affected). The agent knows about useful flags like --configuration, --parallel, and how to filter by project patterns or tags.
This also extends to the plugin ecosystem. The nx-plugins skill teaches the agent to discover available plugins with nx list and install them with nx add, suggesting the right plugins where they can enhance your developer experience.
Monorepo Best Practices
Beyond Nx-specific skills, we also ship skills that help your agent navigate common monorepo pitfalls. A good example: AI agents frequently fail at linking packages across a monorepo because they don't know your package manager's workspace syntax. The link-workspace-packages skill handles pnpm, yarn, npm, and bun, using the correct workspace protocol for each.
This Is Just the Start
This is the first release. We're going to keep expanding the skills based on how people use them. If your AI agent fails at a task or behaves suboptimally in your Nx or monorepo workspace, open a feature request or submit a PR to the skills repo. We want to hear what workflows matter most to you.